简介 The pBAD Directional TOPO Expression Kit utilizes a highly efficient, 5-minute cloning strategy ("TOPO Cloning") to directionally clone a blunt-end PCR product into a vector for soluble, regulated expression and simplified protein purification in E. coli. Blunt-end PCR products clone directionally at greater than 90% efficiency with no ligase, post-PCR procedures, or restriction enzymes required. In addition, pBAD202/D-TOPO vector contains the His-Patch (HP) thioredoxin leader for increased translation efficiency and solubility of recombinant fusion proteins. Expression in E. coli is driven by the araBAD promoter (PBAD). The AraC gene product encoded on the pBAD202/D-TOPO vector positively regulates this promoter. pBAD202/D-TOPO 载体特征 pBAD202/D-TOPO is designed to facilitate rapid, directional TOPO Cloning of blunt-end PCR products for regulated expression in E. coli. Features of the vector include:
araBAD promoter (PBAD) for tight, dose-dependent regulation of heterologous gene expression
N-terminal His-Patch thioredoxin for increased translation efficiency and solubility of heterologous proteins
Directional TOPO Cloning site for rapid and efficient directional cloning of a blunt-end PCR product
C-terminal fusion tag for detection and purification of recombinant fusion proteins Kanamycin resistance gene for selection in E. coli
araC gene encoding a regulatory protein for tight regulation of the PBAD promoter
pUC origin for maintenance in E. coli.
Note: Although the pBAD202/D-TOPO vector contains a pUC origin, they act as lowcopy
number plasmids, resulting in lower yields of the vectors. L-阿拉伯糖调控表达 In the presence of arabinose, expression from PBAD is induced while only very low levels of transcription are observed from PBAD in the absence of arabinose (Lee, 1980; Lee et al., 1987). Uninduced levels are repressed even further by growth in the presence of glucose (0.1% to 0.2%). Glucose reduces the levels of 3′, 5′-cyclic AMP, lowering expression from the catabolite-repressed PBAD promoter (Miyada et al., 1984). By varying the concentration of arabinose, protein expression levels can be optimized to ensure maximum expression of protein. In addition, the tight regulation of PBAD by AraC is useful for expression of potentially toxic or essential genes (Carson et al., 1991; Dalbey and Wickner, 1985; Guzman et al., 1992; Kuhn and Wickner, 1985; Russell et al., 1989; San Millan et al., 1989). For more information on the mechanism of expression and repression of the ara regulon, see page 33 or refer to Schleif, 1992. 硫氧还蛋白 The 11.7 kDa thioredoxin protein is found in yeast, plants, and mammals, as well as in bacteria. It was originally isolated from E. coli as a hydrogen donor for ribonuclease reductase (see Holmgren, 1985 for a review). The gene has been completely sequenced (Wallace and Kushner, 1984). The protein has been crystallized and its three-dimensional structure determined (Katti et al., 1990). When overexpressed in E. coli, thioredoxin is able to accumulate to approximately 40% of the total cellular protein and still remains soluble. When used as a fusion partner, thioredoxin can increase translation efficiency and, in some cases, solubility of eukaryotic proteins expressed in E. coli. Examples of eukaryotic proteins that have been produced as soluble C-terminal fusions to the thioredoxin protein in E. coli (LaVallie et al., 1993) include:
Murine interleukin-2
Human interleukin-3
Murine interleukin-4
Murine interleukin-5
Human macrophage colony stimulating factor
Murine steel factor
Murine leukemia inhibitory factor
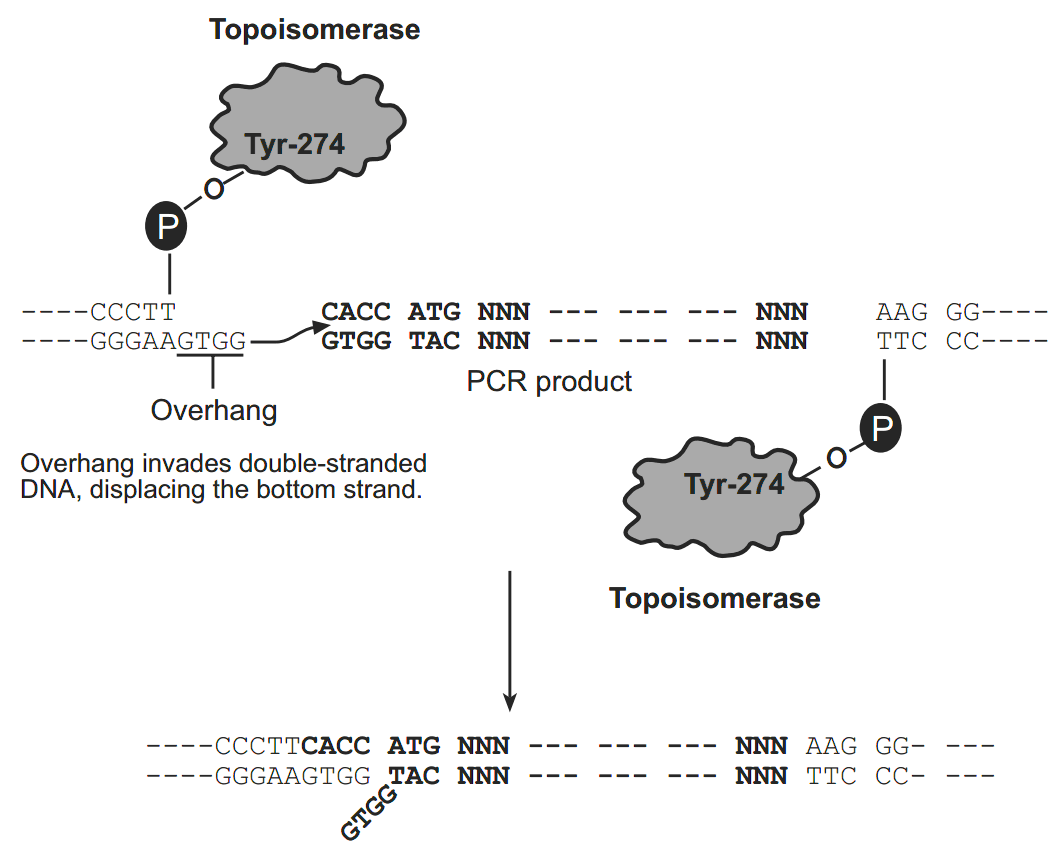
Human bone morphogenetic protein-2 HP-硫氧还蛋白 The thioredoxin protein has been mutated to contain a metal binding domain, and is termed “His-Patch thioredoxin”. To create a metal binding domain in the thioredoxin protein, the glutamate residue at position 32 and the glutamine residue at position 64 were mutated to histidine residues. When His-Patch thioredoxin folds, the histidines at positions 32 and 64 interact with a native histidine at position 8 to form a “patch”. This histidine patch has been shown to have high affinity for divalent cations (Lu et al., 1996). His-Patch thioredoxin (HP-thioredoxin) proteins can therefore be purified on metal chelating resins (e.g. ProBond). How Directional TOPO Cloning Works Topoisomerase I from Vaccinia virus binds to duplex DNA at specific sites and cleaves the phosphodiester backbone after 5-CCCTT in one strand (Shuman, 1991). The energy from the broken phosphodiester backbone is conserved by formation of a covalent bond between the 3 phosphate of the cleaved strand and a tyrosyl residue (Tyr-274) of topoisomerase I. The phospho-tyrosyl bond between the DNA and enzyme can subsequently be attacked by the 5 hydroxyl of the original cleaved strand, reversing the reaction and releasing topoisomerase (Shuman, 1994). TOPO Cloning exploits this reaction to efficiently clone PCR products.
Directional TOPO Cloning
Directional joining of double-strand DNA using TOPO-charged oligonucleotides occurs by adding a 3 single-stranded end (overhang) to the incoming DNA (Cheng and Shuman, 2000). This single-stranded overhang is identical to the 5end of the TOPO-charged DNA fragment. At Invitrogen, this idea has been modified by adding a 4 nucleotide overhang sequence to the TOPO-charged DNA and adapting it to a ‘whole vector’ format.
In this system, PCR products are directionally cloned by adding four bases to the forward primer (CACC). The overhang in the cloning vector (GTGG) invades the 5 end of the PCR product, anneals to the added bases, and stabilizes the PCR product in the correct orientation. Inserts can be cloned in the correct orientation with efficiencies equal to or greater than 90%.